
Glossary
Discover the key words of the platform
A
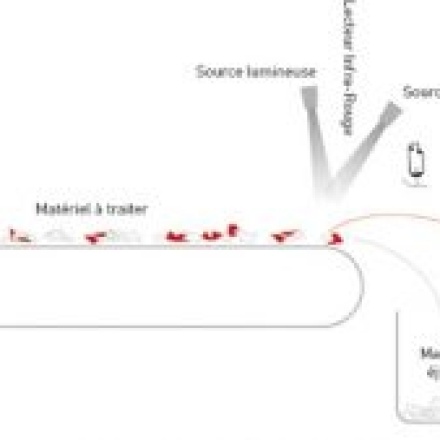
Automatic sorting
Automated product sorting process based, among other things, on optical sorting using spectroscopy such as near infrared (NIR) to facilitate characterization (shape, composition, color) with a view to recycling.
Antifungal treatment
Treatment to prevent the appearance of mold and mildew.
Airlay laying
Nonwovens manufacturing stage: mechanical process of pneumatically coating fibers (and adhesive particles) to produce a randomly oriented fibrous web. The Airlay process produces nonwovens from 250 to 4,000 g/m2; while the Airlaid process produces nonwovens below 250 g/m2, with shorter fibers.

Additive manufacturing (3D)
All the processes used to manufacture a physical object from a digital object, layer by layer, by adding material, such as 3D printing.

Additives
In plastics manufacturing, raw materials may require the addition of organic or mineral compounds, often in small proportions, to enable the material to be processed, improve it or give it certain properties. These additives include: plasticisers, colourants, catalysts, flame retardants, stabilisers, lubricants, antistatic agents, fungicides, etc.

Airlay
Process of Airlay laying.
Activities
Main categories of activity for companies on the platform.
C
Clothing, Household Linen, Footwear (CHR)
All Apparel Textiles (synthetic and/or natural textile garments, excluding professional uniforms), Household Linen (excluding upholstery fabric) and Footwear.
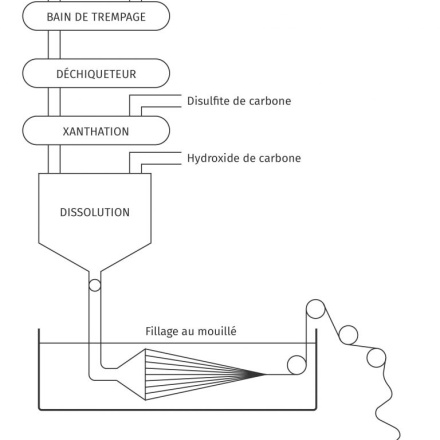
Cellulose / viscose regeneration
Production of regenerated cellulose (such as viscose and cellophane) from dissolving cellulose pulp, derived from wood or cellulose-based textile waste such as cotton.
Closed-loop recycling
Any recycling operation enabling the reuse of recycled fibers from CHR waste in the production of new CHR.
Cellulosic pulp production
The preparation of cellulose pulp involves isolating the cellulose fibers contained in wood fibers, waste paper or cellulose textiles such as cotton, using a chemical process. The cellulose pulp to be dissolved is the basic ingredient for paper manufacture and industrial viscose production.

Collection operator / Collector
Operator responsible for the logistics of collecting the contents and/or surplus of used CHR recovered from a Point d'Apport Volontaire. An operator may or may not be both collection operator and voluntary drop-off point holder.
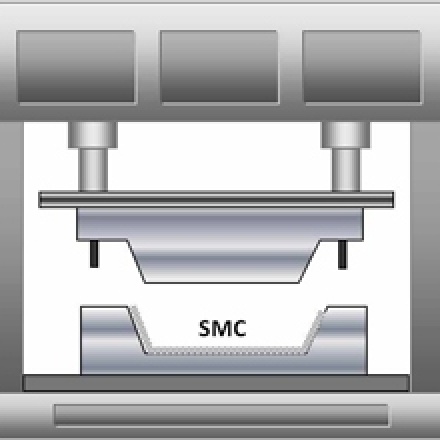
Compression molding
Processes for manufacturing composite parts, e.g. prepregs using SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) or BMC (Bulk Molding Compound).
Carded spinning
Successive operations to transform textile fibers into yarn: carding, roving and then threading.
Chemical spinning
The process of restructuring fibers into weaving yarns.
Cellulosic fiber
- Natural: cotton, linen, hemp. - Artificial: Viscose, Modal, Polynosic, Tencel®, Lyocell®.
Coating
Application of a surface treatment (lacquer, paint, oil, resin, etc.) to a substrate (paper, textile, plastic film, metal, etc.).
Chemical dissolution
Dissolving synthetic or artificial fibers in a specific solvent or solvents to recover the original constituents without damaging their chemical structures.
Container
Containers made available to residents in public spaces (streets, waste collection centers, etc.), or in private spaces (parking lots, stores, supermarkets, etc.) for depositing used CHR. They are designed to withstand the elements and protect clothing from damp and dust.
Compressing
Action for shaping coarse aggregates.
Compounding
The process of amalgamating residues from the shredding of synthetic textiles to produce aggregates for the plastics industry.
Collection by container
Voluntary collection operation by containers dedicated to the collection of clothing, footwear and household linen. These containers are made available to households in public or private spaces. The collection operator organizes and collects the tonnages deposited in these containers.
Consumer citizen
A person who buys clothes, household linen and shoes and part with them when they are no longer needed, or to make room in their closets.
Charges
Additives in the form of pulp, powders or textile fibers for obtaining specific characteristics in all types of polymers (fibers, composites)
Carding
Parallelize textile fibers and form veils to create a yarn.
Characteristics
Product/material characteristics in terms of used flow (= post-consumer), sources, format, packaging and/or quantity (weight).
Calendering
Textiles: finishing process used to smooth, coat or thin a material. Other industries: plastic deformation of various materials in paste form, obtained by compression between 2 counter-rotating cylinders (rolling mill).
Coarse grinding / shredding
An operation equivalent to mechanical needle-punching, shredding involves reducing the size of different types of material to chippings of the order of a few cm or mm.

CHR shops
Private shops/retailers who can potentially take back used CHR, offering them valorisation opportunities.
D
Densimetric separation
Dry or wet separation process based on relative density, i.e. the ratio of the density of one body to the density of another body taken as a reference.

Dedicated space at the waste collection center
Premises, containers or bins specially designed for depositing used CHR at waste collection centers. The space may be self-service, or managed by the site wardens.
Disposal
Treatment of final waste, including storage or incineration.
Devulcanization
A method for processing elastomers (natural or synthetic rubber) that recovers the initial polymer by reversing the vulcanization process, without chemical additives and without degrading the macromolecular chains, unlike grinding.

Depolymerization
The process of converting a polymer into a monomer or a mixture of monomers.
Densification
Action of increasing the density of granules, to obtain a viscosity index suitable for extrusion or injection.

Disassembling
Dismantling garments to remove hard spots (buttons, rivets, zippers, patches, etc.).
Delamination
Process for separating different materials from a product with several successive layers of material.
Door-to-door collection
Home collection operation organized by a collection operator to recover clothing, household linen and shoes.
Downstream scale
Rules and amounts for Refashion's financial support paid to sorting operators and local authorities.

Downstream of the industry
All players involved in collection, sorting, reuse and elimination operations, as well as local authorities.
E
Energy valorisation
Waste treatment operation enabling energy production. A non-hazardous waste incinerator carries out an energy recovery operation if it complies with the conditions defined in article 33-2 of the modified decree of September 20, 2002 on non-hazardous waste incineration and co-incineration plants. One of these conditions is the achievement of an energy yield that must be greater than or equal to 0.65 or 0.6, depending on the type of facility (see Annex VI of the aforementioned decree, and MEDDE Glossary, p. 30).
Extrusion of profiles, tubes or other forms
Processing thermoplastics by melt compression through a die to obtain a rod, a hollow tube or a more complex profile, e.g. window frame profiles.
Eliminator
It treats textiles that have not been recycled and are considered as final waste.
Eco-modulation
Modulation of the upstream scale, in the form of a bonus-malus system, based on product eco-design criteria with regard to end-of-life and recyclability.
Eco-design
Designing a product to reduce its environmental impact by taking into account the various stages of its life cycle, including its end-of-life.
Enzymatic dissolution
- Recycling of fermentable organic products characterized by their biodegradability, leading to composting and methanization. - Textile recycling through enzymatic treatment and decomposition of polymers to form textile filaments.
End destination
Final destination of used CHR.

F
Flame-retardant treatment
Flame-retardant treatment.
First Sort
This operation classifies the raw collection product and separates : - elements (the mix) intended for recovery through re-use, - elements destined for recycling - final waste from sorting
Fusion
Melting, passage of a body or substance from a solid to a liquid state, usually under the action of heat.

Flock
Short textile fibers (1 to 5 mm) obtained by grinding textiles. Used for covering (e.g. faux snow, suede, flocking).
Flocking
Spray coating process for short fibers obtained by grinding textiles.
Filage
Extrusion de (multi)filaments continus. Plusieurs procédés existent suivant le type de fibre à produire : voie solvant (ou humide), voie fondue.
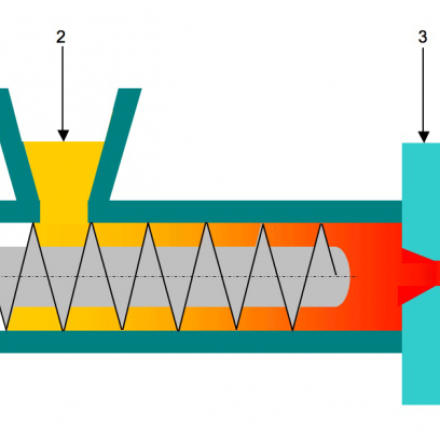
Functional specifications
Document issued by the public authorities detailing Refashion's operating obligations.
Fine grinding
Refining of shreds into textile pulp.
Fibrous fillers
Additives in the form of pulp, powders or short textile fibres to obtain specific characteristics in all types of polymers (plastics, composites, concrete).

G
Grading
Also known as sorting. Manual sorting and grading of collected used textiles and footwear, with a view to their specific treatment (reuse, recycling, disposal).
Geotextile
Fabric generally made of synthetic materials for use in construction, civil engineering and agriculture. Its special feature is that it is porous.
Grinding
The process of reducing used CHR by grinding them into short fibers or powders.
H
Hard spots
Buttons, zippers, velcro, rivets, etc.
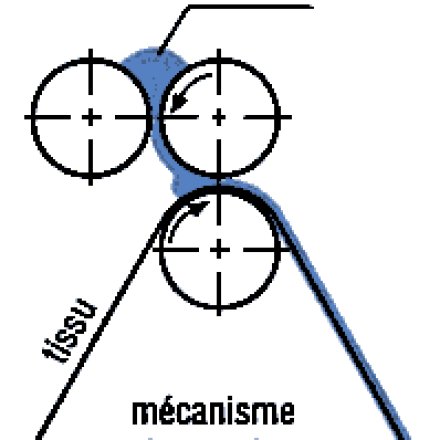
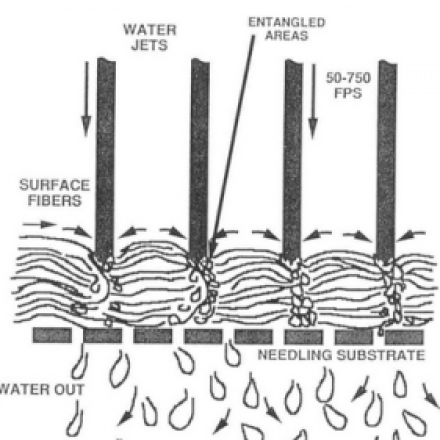
Hydroentanglement / spunlacing
Hydroentanglement, or spunlacing, is based on the same principle as needling, i.e. the physical entanglement of fibers without the use of binders or adhesives, to produce a non-woven fabric.
I
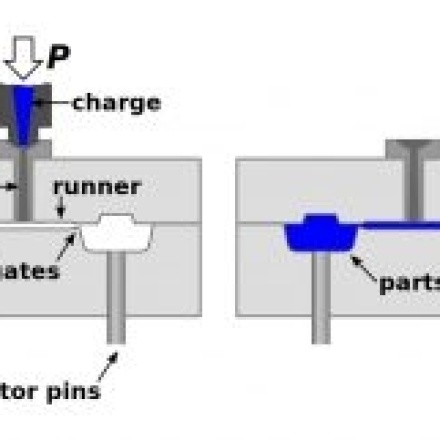
Injection
Method for processing thermoformable materials, especially thermoplastics, by means of an injection molding machine comprising an ad hoc mold to obtain finished parts.
L
Logo trademark of the industry
Logo present on all voluntary drop-off point identified by the sector. Their presence on a voluntary drop-off point indicates to the public that they can dispose of their CHR in complete confidence.
Large scale composting
Process for accelerated aerobic treatment of large quantities of fermentable materials in the form of fertilizer.

Local authority
Municipality, community of communes or EPCI (public establishment of intercommunal cooperation), the local authority informs its citizens, coordinates collection and encourages them to take part in sorting and recycling used CHR.
Local association branch
Association taking back used CHF on their premises at at specific times.
M
Material valorisation
A waste treatment operation that combines Reuse, Recycling (wiping and shredding in the case of CHR waste) and the manufacture of materials such as substitute fuels (e.g. solid recovered fuels) or fill materials (MEDDE Lexicon, p. 29-30). It is distinct from energy recovery, although the manufacture of substitute fuels is a possible preparatory operation for energy recovery.
Material sorting
Operations to separate textile waste and/or its components for recycling into new products or materials.
Manual material sorting
Manual sorting of non-reusable products by type of material(s) for recycling.

Manual color sorting
Manual separation of products by color family.

Magnetic separation
Magnetic separation is a technique for separating analytes from various types of matrices according to their behavior in relation to a magnetic field.

Metal removal
An eddy current separator is used to magnetically extract non-ferrous metals from a material stream, from which ferrous metals are extracted upstream via a magnet system.

Mechanical pressing
The process of applying sufficient pressure to change the density of textiles to form new products without the addition of binders.
Micronization
Operation consisting in grinding or crushing a solid to a very fine powder. The particles obtained can vary from 10 to a few hundred micrometers.
Marketers
Any natural or legal person who places new textile products for clothing, household linen and footwear (CHR) intended for households on the national market on a professional basis, in accordance with article L 541-10-3 of the French Environment Code. A marketer may be a manufacturer, importer or distributor of such products.
Mixing / dosage
Fibers or polymers are mixed with other measured substances - fillers, plasticizers, additives, etc. - to produce a new material.

Markets
Industrial markets for materials, semi-finished and finished products offered on the platform.
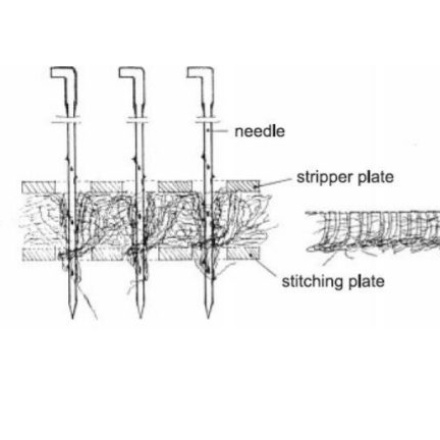
Mecanic needle-punching
Mechanical consolidation technique for nonwovens using needles to create a physical entanglement of fibres between the layers and hold them together. The resulting products are felts of varying degrees of density.
Members
Natural or legal persons who market textile products (clothing, new household linen and footwear) to private individuals and, as such, pay a contribution to Refashion.
N
Nonwoven
Formation of fiber coating.
Needle-punching
Making a yarn by entangling threads with needle rollers.
O
Other separation processes
Open-loop recycling
Any recycling operation enabling the reuse of recycled fibers from CHR waste in the production of new products, excluding CHR.
Outgoing products
An outgoing product or "output" is the category of product offered by companies on the platform, resulting from their production / transformation process.
Open-end spinning
Successive operations for transforming textile fibers into yarn: carding, making the sliver and then the yarn in a turbine.
On-site collection
Textiles brought by households to voluntary collection points.
P
Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO)
Obligation on producers, importers and distributors of waste-generating products (or the elements and materials used in their manufacture) to provide or contribute to the disposal of said waste, in accordance with article L 514-10-3 of the French Environment Code.
Products / Materials
Materials, semi-finished and finished products derived in whole or in part from the recycling of textiles and footwear, or to be recycled, offered by companies on the platform.
Polymer blends
A macroscopically homogeneous blend of two or more polymers. The most common category is immiscible (heterogeneous) polymer blends.
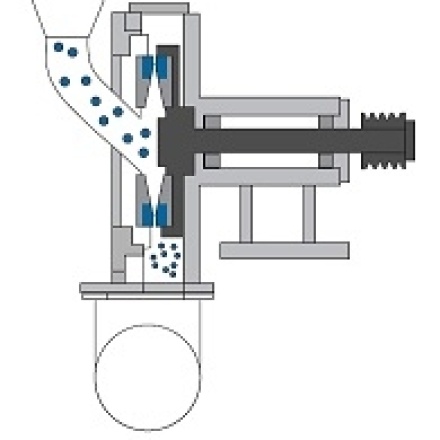
Pelletizing
Process by which material is transformed into granules.
R
Recycling Solutions / Competences
Processing stages for non-reusable textiles/shoes.
Reusing
Any operation by which substances, materials or products that have become waste are used again for the same purpose. It takes place after a sorting operation (article L 541-1-1 of the French Environment Code).
Reuse
Waste prevention action whereby substances, materials or products are reused for the same purpose for which they were conceived. This concept is close to the notion of "reuse", but differs from it in that it concerns products that have not gone through the status of waste.
Recyclor
Operator who transforms textiles that cannot be reused as they are, into raw materials to be used in the manufacture of new products (clothing, packaging, insulation, padding, etc.).
Recycling
A material recovery operation whereby waste [...] is reprocessed into substances, materials or products for its original function or for other purposes. Waste-to-energy operations, waste-to-fuel operations and landfill operations do not qualify as recycling operations (article L 541-1-1 of the French Environment Code).
Residual household waste
Refers to waste remaining after separate collections. This waste fraction is sometimes referred to as "grey garbage can". The composition of residual household waste varies from place to place, depending on the type of collection.
Removing 'hard spots'
Remove all disruptive destructuring elements: buttons, zippers, velcro, rivets, etc.
Raw collection
"Raw collection" or "original" is the flow of used CHR collected at voluntary collection points before any sorting operation. It will be sorted for reuse, rag transformation, shredding or energetic revalorisation.
S
Sorting
Operation to separate used CHR collected separately, with a view to their final treatment by "Recovery" or "Disposal" (see definitions).
Synthetics
Fibers obtained by polymerization or polycondensation of monomers derived from petroleum.
Simple sorting
See Skimming.
Second waste
Sorting of mixed items for reuse. Sorting by quality, degree of wear, type of garment, gender, size and season, etc...
Spraying
The action of projecting or spreading a powdery solid or liquid in the form of very fine particles, using a pressure device, in a uniform manner.

Sorting operator/ Sorter
Operator of a sorting facility for used CHR, collected separately in accordance with the provisions of chapter 3 of the approved eco-organization's specifications.
Skimmed
Raw from collection or original from which the "cream" has been removed or "first quality" used CHR intended for re-use.
Skimming
This operation consists of extracting the "cream" from the raw material collected. This cream is resold in its original state in thrift stores or community stores in France or abroad. This operation does not constitute a sorting operation likely to be financially supported by the eco-organization.
Shoes dismantling
Action of separating the various components of footwear (e.g. by delamination, tearing or cutting).
Shoe cutting
System for cutting (felt/fleece) into different shapes or (shoes) into different sections (upper, insole, outsole).

Shredding
Process of successive cutting of textiles to obtain chippings.
T
Treatment
Waste management operation which consists in recovering or eliminating waste. This may include operations preparatory to recovery or elimination, such as sorting (cf. article L 541-1-1 of the Environment Code and the waste prevention and management plan).
Thermoforming
Shaping plastic products.
Thermo-compression
Compression combining pressure and heat.
Thermobonding
Manufacture of more or less rigid sheets, bonded by heating and calendering synthetic fibers.
Thermal induction
Induction heat treatment of nonwovens is a consolidation process in which the fibers are softened in a hot gas or between heated rollers, or simply blown through with hot air.
Textile industry
All upstream and downstream players involved in the CHR sector.
Tearing
The process of transforming textiles into long fibers by passing them through a fraying machine. These fibers can then be woven again, or used as cushion stuffing or insulation.
Trims removal
Remove garment trimmings such as hard points (buttons, zippers, rivets, etc.), labels or excess thickness (velcro, seams, etc.), which are considered disruptive to recycling.

Textile waste
All waste from clothing textiles, household linen and footwear produced by households.
The cream
Good-quality CHR that can be reused and/or easily resold on the second-hand market.
Textile cutting
Cutting textiles to size for wiping cloths. Also used to remove trimmings such as buttons, zippers, labels and excess thickness (pockets, etc.).

Textile/shoe collection
All textile and footwear collection operations.
U
Unravelling
Mechanical process of successively stretching textiles to extract long fibers for spinning. Process equivalent to tearing, but less aggressive.

Ultimate waste
Sorted residual waste: all waste that cannot be reused or recycled. It is then incinerated or stored.
Upstream scale
Rules and amounts of contributions paid to Refashion by its members.
Upstream of the industry
All marketers.
V
Viscose
Cellulose fiber obtained from the pulp of wood or other plants.
Valorisation
Waste treatment operation whose main result is that waste is used for a useful purpose in substitution for other substances, materials or products which would have been used for a particular purpose, or that waste is prepared for use for this purpose, including by the waste producer". Recovery is distinct from disposal. It encompasses "material recovery" and "energy recovery" (see definitions below) (cf. article L 541-1-1 of the Environment Code and MEDDE Glossary, p. 29 and 31).
Voluntary drop-off point
Address where people can drop off their used CHR. It may correspond to : - the presence of containers on the public highway, in a private space, at a waste collection center, - a used CHR recovery facility in an association's premises, or a CHR sales outlet, - a CHR recovery event in the marketplace or at a market, - door-to-door collection.
Voluntary drop-off point holders (DPAV)
Individual or legal entity owning : - a voluntary drop-off point at the address mapped in the Refashion database, - private or public titles authorizing the operator to install a voluntary drop-off point at this location. An operator may or may not be both a voluntary drop-off point holder and a collection operator.
W
Water-repellent treatment
Anti-permeability treatment.
Web bonding
Formation of a web by carding fibers.
Waste management
This activity covers "the collection, transportation, recovery and disposal of waste and, more broadly, any activity involved in organizing the management of waste from its production to its final treatment [...]" (Article L 541-1-1 of the French Environment Code). It includes waste collection and treatment, and is distinct from waste prevention.



